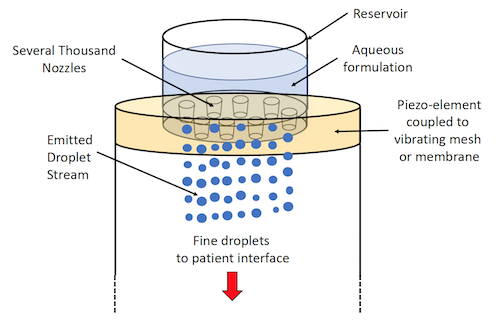
Choices and features of the different available nebulizer systems
Nebulizing systems available today vary widely in terms of medication delivery characteristics and sophistication of the associated controls for optimizing performance in terms of both delivery rate and droplet size distribution. The primary categories of nebulizers are:
- Pneumatic, or “jet,” nebulizers
- Continuous
- Breath enhanced with conservation of medication
- Breath enhanced without conservation of medication
- Breath actuated
- Vibrating mesh/membrane
- Ultrasonic
- “Smart”
- With breath control
- Without breath control
Pneumatic nebulizers
Price range: $ – $$
These are generally the lowest cost options, with continuous jet nebulizers, which have very simple designs, at the lowest end of the cost scale. The CareFusion Misty Fast nebulizer is an example of this type of nebulizer.
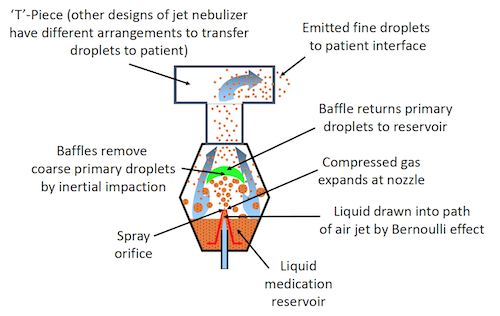
Breath enhanced pneumatic nebulizers such as the PARI LC Plus and Sprint nebulizers and breath actuated pneumatic nebulizers such as the Trudell/Monaghan Aeroclipse II, which offer higher efficiency, and in the case of breath actuated devices, better compliance and low fugitive emissions, are slightly more complicated and therefore slightly more expensive, but still relatively low cost compared with nebulizers that have electronic controllers to operate.
Medication delivery profiles for different types of pneumatic (jet) nebulizers:
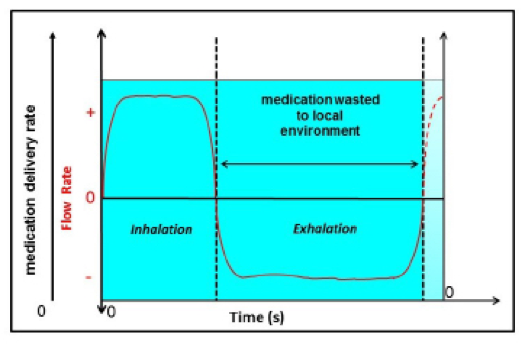
Continuous delivery of medication 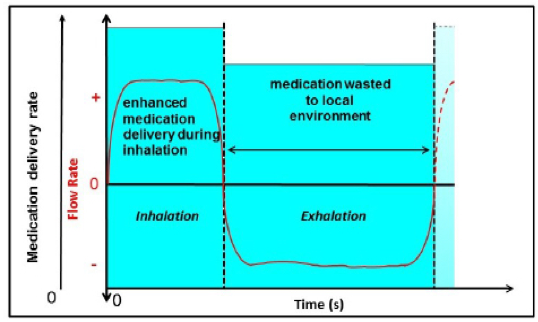
Breath-enhanced without conserving medication during exhalation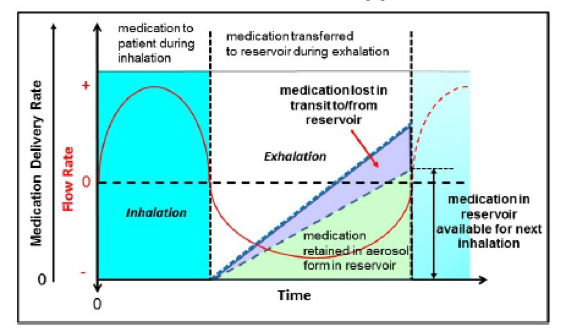
Breath enhanced without conserving medication during exhalation 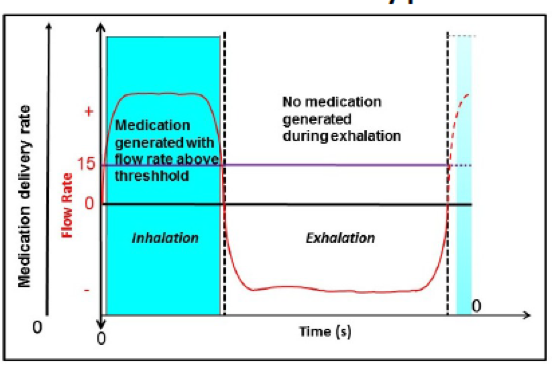
Breath actuated
For home use, pneumatic nebulizers can be used with a compressor pump powered by the house’s main power source or by battery; for hospital use, these nebulizers are normally powered by compressed gas.